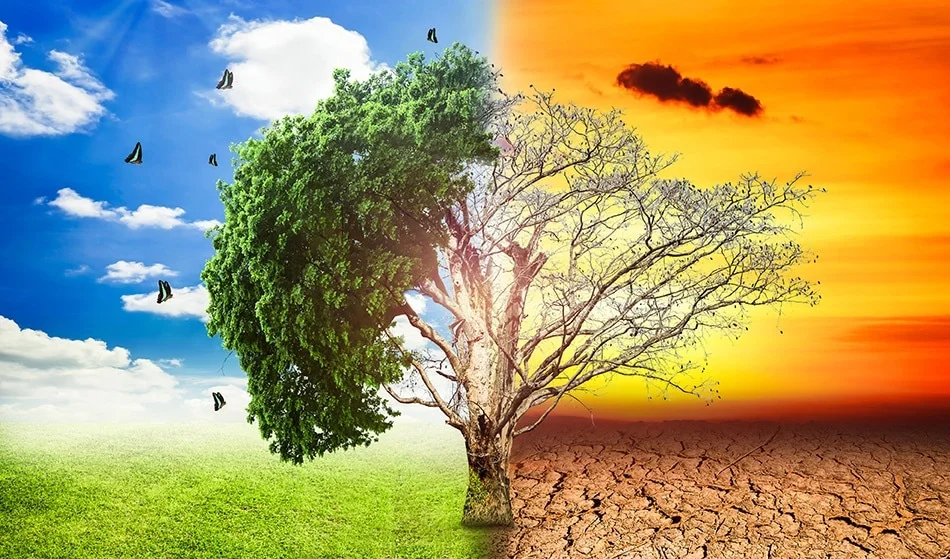

Climate Change And Global Warming
Climate Change and Global Warming
One of the primary drivers behind the surge in heatwaves is climate change, resulting from human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation. The release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere traps heat, leading to a rise in global temperatures. As a consequence, extreme weather events, including heatwaves, become more frequent and severe.
Urbanization and Heat Island Effect
The rapid urbanization of cities has exacerbated heatwaves through the heat island effect. Asphalt, concrete, and other building materials absorb and retain heat, causing urban areas to become significantly warmer than surrounding rural regions. This urban heat island effect intensifies heatwaves, especially during the nighttime when heat is released slowly, impacting the health and comfort of urban dwellers.

Urbanization And Heat Island Effect
Changes in Atmospheric Circulation Patterns
Shifts in atmospheric circulation patterns, such as jet streams and high-pressure systems, can influence the occurrence and intensity of heatwaves. Climate change can disrupt these patterns, leading to the persistence of high-pressure systems that trap warm air, prolonging heatwave events.
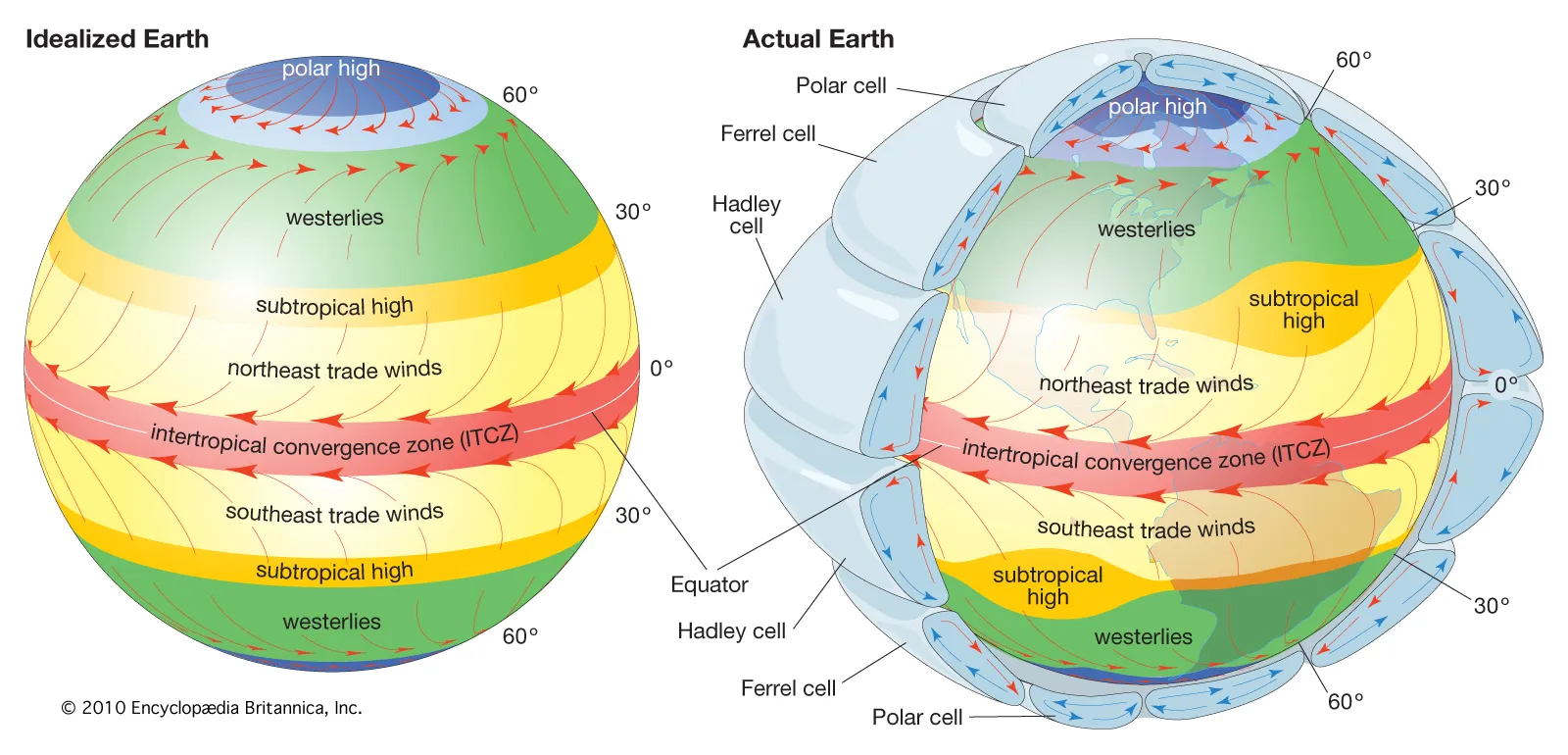
Changes In Atmospheric Circulation Patterns
Ocean Warming and Heat Transfer
The oceans play a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate. With rising global temperatures, oceans absorb more heat from the atmosphere, contributing to ocean warming. This, in turn, impacts weather patterns, leading to more frequent and intense heatwaves in coastal areas and beyond.
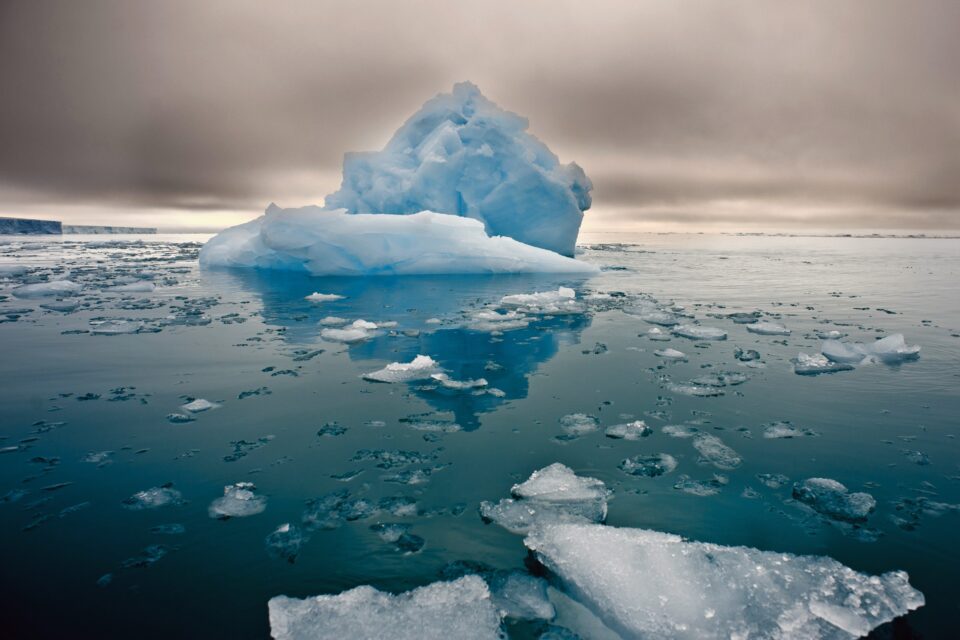

Ocean Warming And Heat Transfer
Feedback Loops and Extreme Weather Events
Climate change can trigger feedback loops that exacerbate heatwaves. For example, melting polar ice reduces the Earth’s albedo, causing it to absorb more sunlight and further warming the planet. Additionally, wildfires resulting from heatwaves release vast amounts of carbon dioxide, amplifying greenhouse gas concentrations and contributing to further warming.
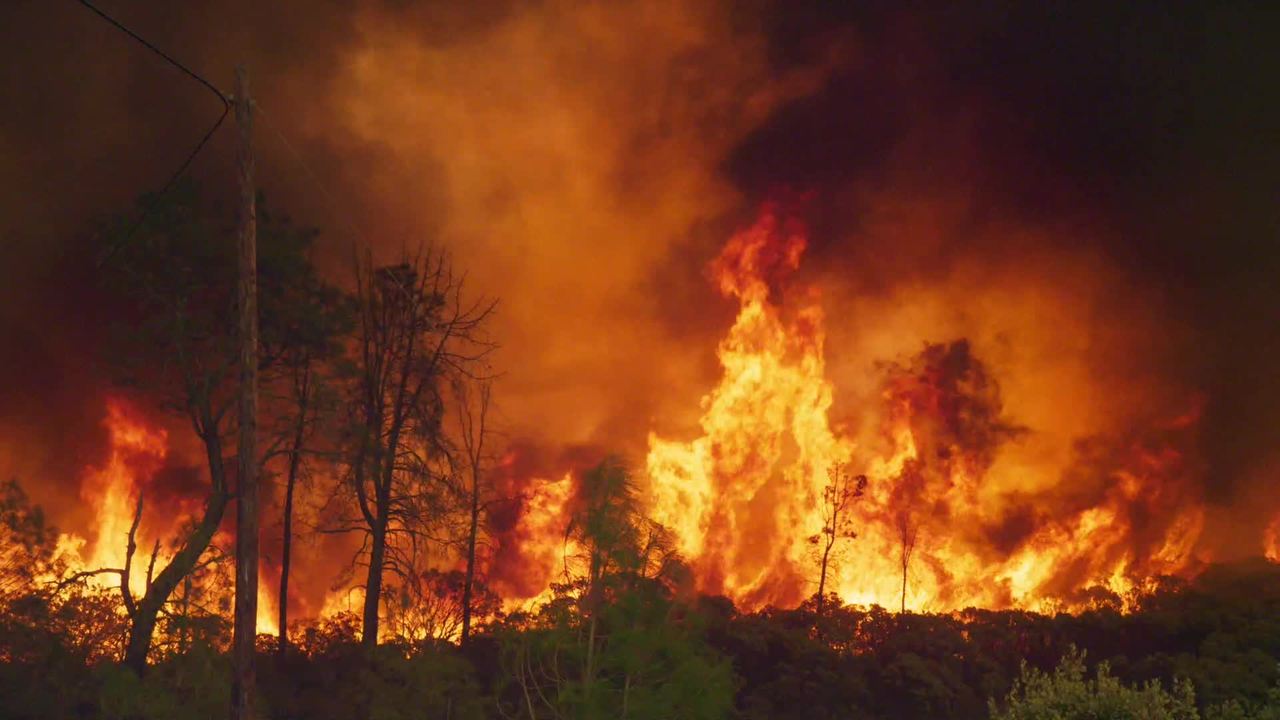

Feedback Loops And Extreme Weather Events
Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies
As heatwaves become more common, communities are faced with the challenge of adapting to these extreme weather events. Effective urban planning, green infrastructure, and sustainable building practices can help mitigate the urban heat island effect. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to renewable energy sources are crucial steps to combatting climate change and reducing the frequency and intensity of heatwaves.
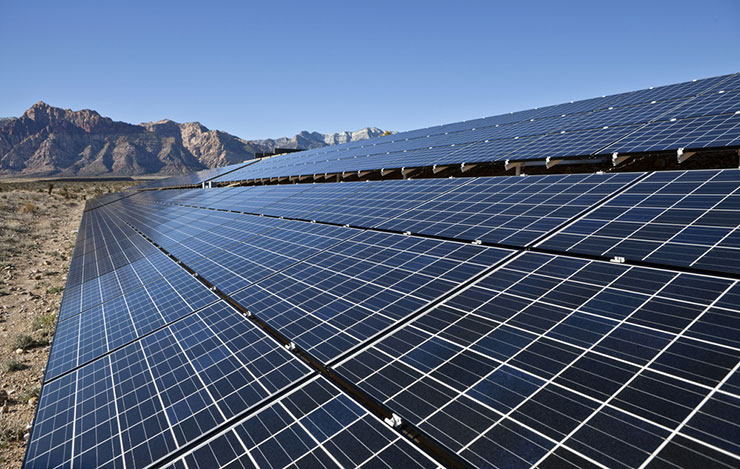

Adaptation And Mitigation Strategies








